Recently, Shanghai Research Institute of Applied Physics, Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, China Institute of Light Sources, Energy and Energy, Rui Rui, respectively collaborated with Professor Jia Chunjiang of Shandong University and Zhang Jun Group of Professor of Inner Mongolia University to characterize using X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy (XAFS). The platform has made progress in confirming the active structure of nickel-based and platinum-based catalysts. Related papers have been published in the American Chemical Society's Physical Chemistry C and Applied Materials and Interfaces magazine (J. Phys. Chem. C, 2016 , 120, 7685-7696; ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8, 18770-18787).
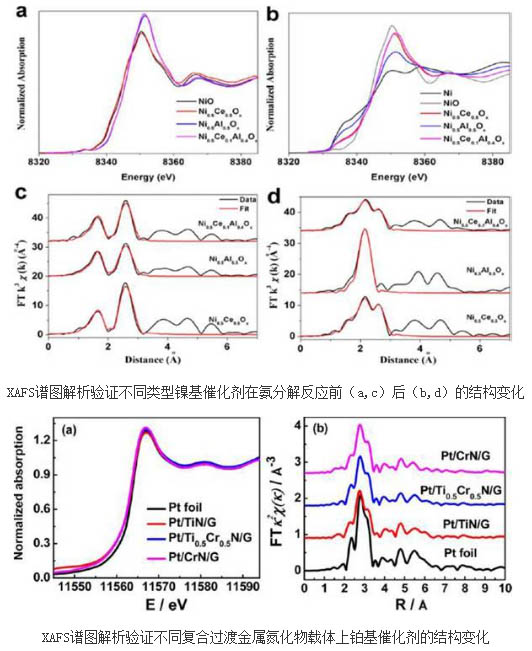
Ammonia decomposition (NH3N2 + H2) is an effective way to produce hydrogen in hydrogen fuel cells. Due to the harsh reaction conditions, it is very difficult to obtain catalysts with high activity and high stability. Jia Chunjiang's research group developed mesoporous multi-metal oxides (Ni-Ce-Al-O) and improved the activity and stability of the ammonia decomposition reaction of nickel-based catalysts; Si Rui's research group passed the XAFS test and analyzed the relevant spectra. It was found that the doping of germanium contributes to the stability of the active metal nickel component. Platinum-based electrode materials are a key part of direct methanol fuel cells, and how to maintain their high catalytic activity under long-term working conditions has become a key scientific issue in this research field. Zhang Jun's group prepared a layered mesoporous material composed of a transition metal nitride and graphene. Metal platinum was supported on the substrate, and its electrocatalytic activity was significantly increased. Si Rui's group passed the XAFS test and related spectra. Graph analysis shows that the formation and stabilization of small-sized platinum nanoparticles is a key factor in the improvement of the performance of platinum-based catalytic materials. The above work results have important guiding significance for the design and synthesis of new nickel-based and platinum-based catalysts and the exploration of related catalytic reaction mechanisms.
Wang Xu, a doctoral student of the Shanghai Department of Light Source Materials and Energy, took part in the above-mentioned research. The relevant XAFS experiments were mainly completed on the Shanghai Light Source BL14W1 line station. The work was jointly funded by the Chinese Academy of Sciences “Hundred Talents Program†project, the National Natural Science Fund, and the strategic pilot nanometer project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Led Flower Stand Light,Led Grain Flower Light,Solar Artificial Flower Light,Tulip Artificial Flower Light
Tianjin Jinji Optoelectronic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.tjjjgd.com